Advanced imaging - CT scanning
Computed Axial Tomography also know as a CAT scan or CT scan for short is an advanced radiographic imaging modality that allows board certified veterinary surgeons like Dr. Davies to acquire 3D images of your pet at extremely high resolution. These three dimensional images can be viewed at any angle and in any plane allowing Dr. Davies to diagnose problems with your pet that cannot be seen with traditional x-ray technology or with an ultrasound scanner.
Northstar Veterinary Surgery has the latest generation high resolution scanner - the GT30 by Vimago. This model is faster and has a larger acquisition area than previous models allowing us to capture the required anatomy quicker than ever before.
In addition to viewing of the images, we can take these high resolution scans and use them to create and print 3D models and guides for surgical planning/modeling that is unique to your pet.
Common Indications for a CT scan
Complex fractures
Pelvic fractures
Skull/Mandibular fractures
Dental imaging
Highly comminuted long bone fractures
Angular Limb Deformities
Assessment and surgical planning
Cutting guides
Templating guides
Neurologic Imaging
IVDD - Intervertebral Disc Disease - very common in Dachshunds and French Bulldogs
Other Spinal cord compressive lesions (Such as cancer)
Brain masses (~80% can be detected)
LS Disease
Vascular anomalies
Portosystemic Shunts
PRAA (Persistent Right Aortic Arch)
Cancer staging/surgical planning
Evaluate invasion of the tumor into surrounding tissues for surgical planning
Metastatic cancer evaluation
Structural Abnormalities
Ectopic ureters
Elbow Dysplasia
OCD lesions
Middle ear disease
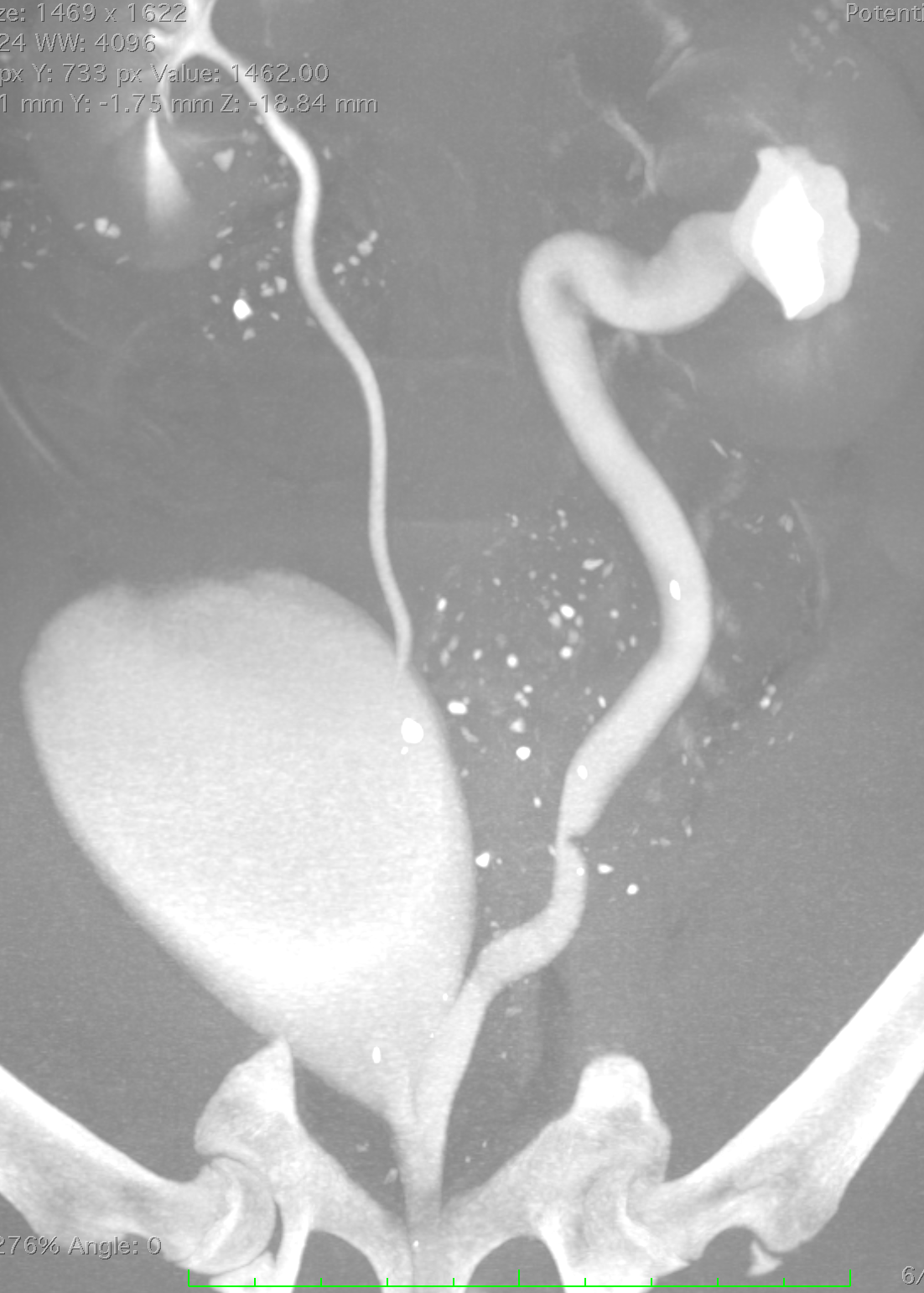
Ectopic ureter study - note the enlarged ectopic ureter to image right compared to the normal ureter on image left.
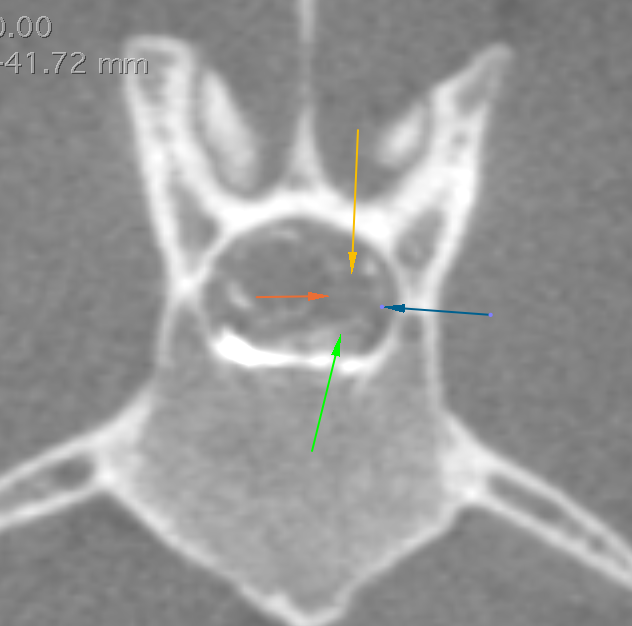
Above images are from a dog with a spinal tumor. The mass was not visible on a plain CT, however is very clear after a myelogram was performed. The arrows denote the mass location. The very white material is the contrast placed in the spinal cord CSF.
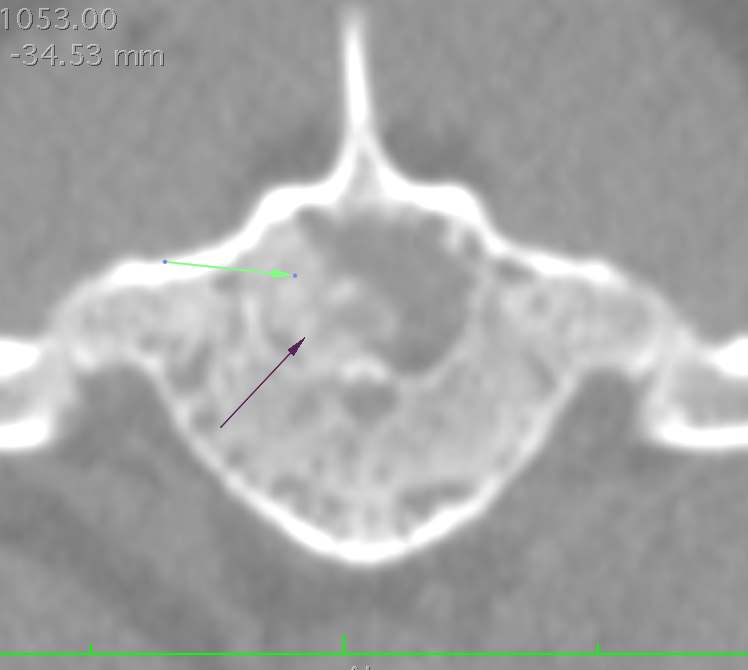
Sagittal (top), axial (bottom) and coronal (left) images of an extruded disc from a dog with IVDD. Arrows denote extruded disc material in axial and coronal images. The red arrow in the top image shows a heavily mineralized disc that has not yet ruptured. The green arrow shows the diseased disc space.